 |
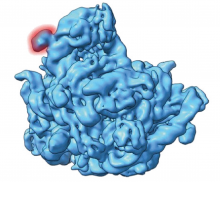
Characterization of SymR and Cryo-EM of Halococcus morrhuae 5S rRNA InsertionTwo papers focusing on the ribosomes were recently published. The first paper highlights the discovery of an area of twofold pseudosymmetry (SymR) within the peptidyl transferase center of the modern ribosome (Rivas and Fox 2020). This observation strongly suggests that the very core of the ribosome arose from a dimerization event between two modest-sized RNAs. It was previously shown that at Read more |
 |
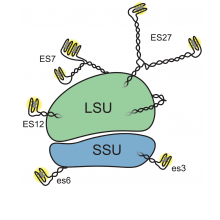
Supersized ribosomal RNA expansion segments in Asgard archaeaThe ribosome is comprised of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and ribosomal proteins (rProteins). The ribosomal common core includes the structurally conserved rRNA and rProtein of all species. The common core connects all life back to the Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA). In eukaryotes, the common core rRNA is elaborated with expansion segments (ESs), making the eukaryotic rRNA longer and more Read more |
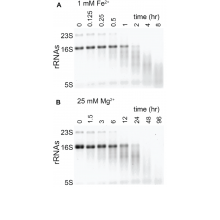 |
Cutting In-line with Iron: Ribosomal Function and Non-oxidative RNA CleavageRibosomes originated long before the Great Oxidation Event (GOE) and their structure and function are strongly dependent on divalent metals (M2+). Thus, understanding ribosomal evolution requires characterization of ribosomal interactions with M2+ ions under pre-GOE conditions: in the presence of abundant Fe2+ and in the absence of O2. Here, we have Read more |
 |
Mutually Stabilizing Interactions Between Proto-peptides and RNACooperative relationships between different classes of biopolymers in today’s biochemistry, such as peptides and nucleic acids, is suggestive of a functional co-evolution between early proto-polymers. Here we show that cationic protopeptides (depsipeptides and polyesters), either produced as mixtures from prebiotic dry-down reactions or synthetically prepared, can engage in direct interactions Read more |
 |
Profusion of G-quadruplexes on Both Subunits of Metazoan RibosomesThe expansion segments on mammalian and bird ribosomes confer increased complexity and mass compared to prokaryotic ribosomes due to the extraordinarily long tentacles. These tentacles appear to be dynamic, switching between G-quadruplex and duplex conformations in response to association with proteins, ions, or other RNAs. Although their conformations remain to be fully resolved, in Homo Read more |
 |
Folding, Assembly And Persistence: The Essential Nature And Origins Of BiopolymersLife as we know it requires three basic types of polymers: polypeptide, polynucleotide, and polysaccharide. The Williams lab has evaluated both universalities and idiosyncratic characteristics of these biopolymers. We have incorporated this information into a model that explains much about biopolymer origins, selection and early evolution. We observe that all three biopolymer types are pre- Read more |
 |
Microbes unveil the mystery of early lifeThe Glass group at Georgia Tech investigates how microbe-metal interactions contributed to maintenance of habitable conditions on Earth, and how the environment influences those microbial metabolisms in return. Why would we focus on the microbial world? The Earth has been constantly inhabited for four billion years. For three-quarters of that time, life was solely microbial. During the first Read more |
 |
Evolutionary Origins of Ribosome DynamicsThe modern ribosome is a dynamic molecular machine comprised of RNA and protein. It is responsible for all coded protein synthesis. A growing peptide is synthesized one residue at a time and when complete it is released from the ribosome. During each round of synthesis, the ribosome itself undergoes a cycle of motions, which facilitate the synthesis and ultimately restore the ribosome to its Read more |
